|
PLUTO
|
|
PLUTO
|
Compute the right hand side of the HD equations in primitive form. More...
#include "pluto.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| void | PrimRHS (double *v, double *dv, double cs2, double h, double *Adv) |
| void | PrimSource (const State_1D *state, int beg, int end, double *a2, double *h, double **src, Grid *grid) |
Compute the right hand side of the HD equations in primitive form.
Implements the right hand side of the quasi-linear form of the hydro equations. In 1D this may be written as
![\[ \partial_t{\mathbf{V}} = - A\cdot\partial_x\mathbf{V} + \mathbf{S} \]](form_44.png)
where 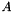 is the matrix of the primitive form of the equations,
is the matrix of the primitive form of the equations, 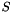 is the source term.
is the source term.
Reference
The function PrimRHS() implements the first term while PrimSource() implements the source term part.
Definition in file prim_eqn.c.
| void PrimRHS | ( | double * | v, |
| double * | dv, | ||
| double | cs2, | ||
| double | h, | ||
| double * | Adv | ||
| ) |
Compute the matrix-vector multiplication 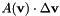 where A is the matrix of the quasi-linear form of the HD equations.
where A is the matrix of the quasi-linear form of the HD equations.
| [in] | w | vector of primitive variables; |
| [in] | dw | limited (linear) slopes; |
| [in] | cs2 | local sound speed; |
| [in] | h | local enthalpy; |
| [out] | Adw | matrix-vector product. |
Definition at line 31 of file prim_eqn.c.
| void PrimSource | ( | const State_1D * | state, |
| int | beg, | ||
| int | end, | ||
| double * | a2, | ||
| double * | h, | ||
| double ** | src, | ||
| Grid * | grid | ||
| ) |
Compute source terms of the HD equations in primitive variables.
The rationale for choosing during which sweep a particular source term has to be incorporated should match the same criterion used during the conservative update. For instance, in polar or cylindrical coordinates, curvilinear source terms are included during the radial sweep only.
| [in] | state | pointer to a State_1D structure; |
| [in] | beg | initial index of computation; |
| [in] | end | final index of computation; |
| [in] | a2 | array of sound speed; |
| [in] | h | array of enthalpies (not needed in MHD); |
| [out] | src | array of source terms; |
| [in] | grid | pointer to a Grid structure. |
Definition at line 71 of file prim_eqn.c.