|
PLUTO
|
|
PLUTO
|
Viscous compressible flow past a cylinder. More...
#include "pluto.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| void | Init (double *v, double x1, double x2, double x3) |
| void | Analysis (const Data *d, Grid *grid) |
| void | UserDefBoundary (const Data *d, RBox *box, int side, Grid *grid) |
Viscous compressible flow past a cylinder.
Set initial and boundary conditions for a flow past a cylinder in 2D cylindrical polar coordinates 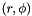 . The cylinder has radius 1 and the domain is initially filled with constant-density and pressure gas with value
. The cylinder has radius 1 and the domain is initially filled with constant-density and pressure gas with value 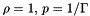 .
.
The velocity field is initialized using the potential flow solution for an inviscid incompressible flow around a cylinder,
![\[ V_r = U\left(1 - \frac{1}{r^2}\right)\cos\theta \,,\qquad V_\phi = -U\left(1 + \frac{1}{r^2}\right)\sin\theta \]](form_267.png)
where U, the far-field velocity, is given by the Mach number. The boundary conditions in phi are periodic while the outer radial boundary is set to inflow for negative values of x while outflow for positive values. A no-slip boundary condition is used at the fluid-solid interface.
The flow past the cylinder, no matter how small the viscosity, will acquire vorticity in a thin boundary layer adjacent to the cylinder. Boundary layer separation may occur leading to the formation of a trailing wake behind the cylinder.
The input parameters are:
g_inputParam[MACH]: sets the upstream Mach numberg_inputParam[NU_VISC]: sets the viscosity

Definition in file init.c.
| void Init | ( | double * | v, |
| double | x1, | ||
| double | x2, | ||
| double | x3 | ||
| ) |
The Init() function can be used to assign initial conditions as as a function of spatial position.
| [out] | v | a pointer to a vector of primitive variables |
| [in] | x1 | coordinate point in the 1st dimension |
| [in] | x2 | coordinate point in the 2nd dimension |
| [in] | x3 | coordinate point in the 3rdt dimension |
The meaning of x1, x2 and x3 depends on the geometry:
![\[ \begin{array}{cccl} x_1 & x_2 & x_3 & \mathrm{Geometry} \\ \noalign{\medskip} \hline x & y & z & \mathrm{Cartesian} \\ \noalign{\medskip} R & z & - & \mathrm{cylindrical} \\ \noalign{\medskip} R & \phi & z & \mathrm{polar} \\ \noalign{\medskip} r & \theta & \phi & \mathrm{spherical} \end{array} \]](form_173.png)
Variable names are accessed by means of an index v[nv], where nv = RHO is density, nv = PRS is pressure, nv = (VX1, VX2, VX3) are the three components of velocity, and so forth.
Definition at line 42 of file init.c.
Assign user-defined boundary conditions.
| [in,out] | d | pointer to the PLUTO data structure containing cell-centered primitive quantities (d->Vc) and staggered magnetic fields (d->Vs, when used) to be filled. |
| [in] | box | pointer to a RBox structure containing the lower and upper indices of the ghost zone-centers/nodes or edges at which data values should be assigned. |
| [in] | side | specifies the boundary side where ghost zones need to be filled. It can assume the following pre-definite values: X1_BEG, X1_END, X2_BEG, X2_END, X3_BEG, X3_END. The special value side == 0 is used to control a region inside the computational domain. |
| [in] | grid | pointer to an array of Grid structures. |
Assign user-defined boundary conditions in the lower boundary ghost zones. The profile is top-hat:
![\[ V_{ij} = \left\{\begin{array}{ll} V_{\rm jet} & \quad\mathrm{for}\quad r_i < 1 \\ \noalign{\medskip} \mathrm{Reflect}(V) & \quad\mathrm{otherwise} \end{array}\right. \]](form_235.png)
where  and
and M is the flow Mach number (the unit velocity is the jet sound speed, so 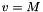 ).
).
Assign user-defined boundary conditions:
x < 1/6 and reflective boundary otherwise.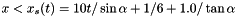 we use fixed (post-shock) values. Unperturbed values otherwise.
we use fixed (post-shock) values. Unperturbed values otherwise. Definition at line 66 of file init.c.