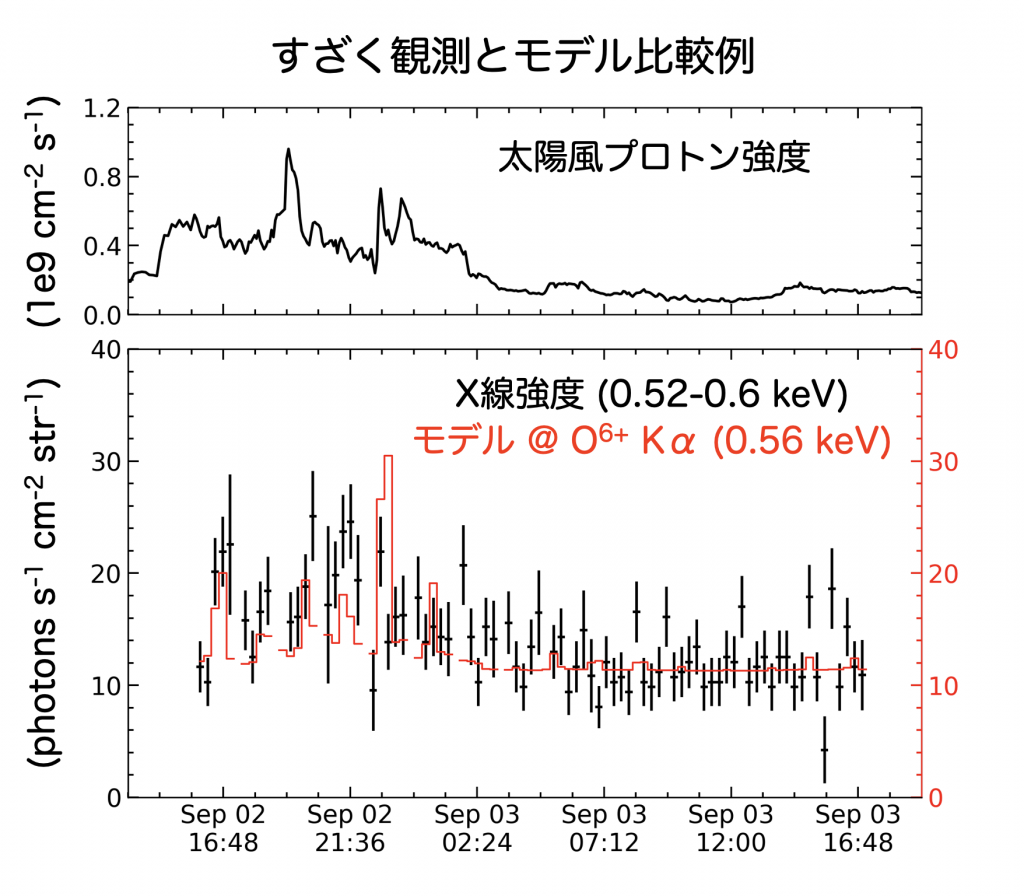
Jun Ishtar (PhD program 3 years) Published in PASJ。Highly ionized ions such as oxygen in the solar wind collide with neutral hydrogen atoms in the Earth's upper atmosphere.、Produces X-ray emission associated with charge exchange reaction。Ishi conducted a systematic analysis of charge-exchange X-ray emissions around the Earth using all public data from the Suzaku satellite.、Built a general-purpose prediction model。Result of comparison with 5 examples of particularly bright light emission、Succeeded in reproducing the average intensity and time fluctuations。Please refer to the following articles for more information。
Fashj: https://doi.org/10.1093/pasj/psac095
arXiV: https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.03844
It should be noted that、Overseas online press release site EurekAlert! I wrote an introductory article for this paper at。Written in plain English for the general public to understand。Please take a look。
EurekAlert! (Press release article) :
https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/958643