The 6-s X-ray pulsar 1E1048.1-5937 was observed by EXOSAT in June 1985 for 20 ks. In this example, we'll conduct a general investigation of the spectrum from the Medium Energy (ME) instrument, i.e. follow the same sort of steps as the original investigators (Seward, Charles & Smale,1986). The ME spectrum and corresponding response matrix were obtained from the HEASARC On-line service.
Once installed, XSPEC is invoked by typing xspec, as in this example on genji, a DEC workstation.
genji% xspec
XSPEC 10.00 12:11:56 12-Nov-96
http://legacy.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/xanadu/xspec/u_manual.html
Plot device not set, use "cpd" to set it
Type "help" or "?" for further information
XSPEC> data s54405.pha
Net count rate (cts/s) for file 1 3.783 +/- 0.1367
using response (RMF) file... s54405.rsp
1 data set is in use
The data command tells the program to read the data as well as the response file that is named in the header of the data file. In general, XSPEC commands can be truncated, provided they remain unambiguous. Since the default extension of a data file is .pha, the above command can be abbreviated to da s54405, if desired. To obtain help on the data command, or on any other command, type help command followed by the name of the command.
One of the first things most users will want to do at this stage--even before fitting models--is to look at their data. The plotting device should be set first, with the command cpd (change plotting device). Here, we use xterm :
XSPEC> cpd /xt
To see a list of alternative plot devices, type cpd ? There are more than 20 different things that can be plotted, all related in some way to the data, the model, the fit and the instrument. To see them, type:
XSPEC> plot ? Choose from the following `plot' sub-commands: data counts ldata residuals chisq delchi ratio summary model emodel eemodel contour efficien ufspec eufspec eeufspec dem insensitv sensitvty Insert selection: (data)
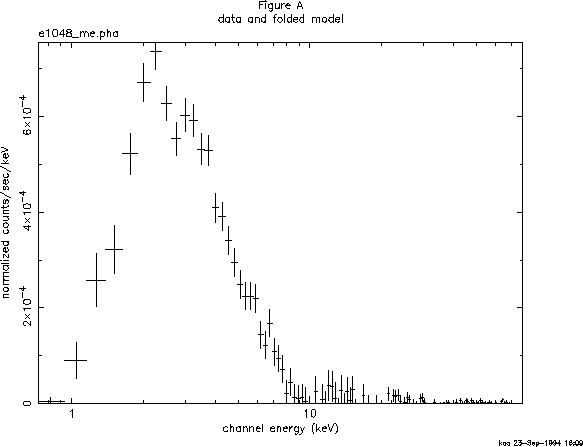
The most fundamental is the data plotted against instrument channel (data); next most fundamental, and more informative, is the data plotted against channel energy. To do this plot, use the XSPEC command setplot energy. Figure A shows the result of the commands:
XSPEC> setplot energy XSPEC> plot data

People familiar with EXOSAT ME data will recognize the spectrum to be soft, absorbed and without an obvious bright iron emission line.
We are now ready to fit the data with a model. Models in XSPEC are specified using the model command, followed by a list of one or more model components chosen from the suite of more than seventy. There are two basic kinds of model: additive models which, after being convolved with the instrument response, prescribe the number of counts per energy bin (e.g., a bremsstrahlung continuum); and multiplicative models, which apply an energy-dependent multiplicative factor to additive models before convolution (e.g., an absorption edge). At least one additive component must be included in the model, but there is no restriction on the number of multiplicative models. To see what components are available, type model ? (for information about a specific component, type help model followed by the name of the component):
XSPEC> model ? Possible additive models are : bbody bbodyrad bknpower bremss c6mekl c6pmekl c6pvmkl c6vmekl cemekl cevmkl cflow compLS compST compTT cutoffpl disk diskbb diskline diskm disko gaussian grbm laor meka mekal mkcflow nteea pegpwrlw pexrav pexriv pltrans powerlaw raymond redge step tita_a useradd1 vbremss vmeka vmekal vmcflow vraymond zbbody zbremss zgauss zpowerlw l_diskfb l_diskh l_diskhr l_photmi rsdist l_smvmkl atable Possible multiplicative models are : absori constant cabs cyclabs dust edge expabs expfac highecut hrefl notch pcfabs phabs plabs smedge spline SSS_ice usermul1 uvred varabs vphabs wabs wndabs zedge zhighect zpcfabs zphabs zvarabs zvfeabs zvphabs zwabs zwndabs l_auabs l_detabs l_ywmod mtable etable Possible mixing models are : ascac Possible convolution models are : gsmooth
Given the quality of our data, as shown by the plot, we'll choose an absorbed power law, specified as follows :
XSPEC> model phabs(powerlaw)
Or, abbreviating unambiguously:
XSPEC> mo pha(po)
Either way, the user is prompted straight away for the initial values of the parameters. Entering <return> in response to a prompt enters the default values. As well as the parameter values themselves, users also may specify step sizes and ranges (value, delta, min, bot, top, and max values), but here, we'll enter the defaults:
XSPEC> mo pha(po)
mo = phabs[1]( powerlaw[2] )
Input parameter value, delta, min, bot, top, and max values for ...
Mod parameter 1 of component 1 phabs nH 10^22
1.000 1.0000E-03 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 1.0000E+05 1.0000E+06
Mod parameter 2 of component 2 powerlaw PhoIndex
1.000 1.0000E-02 -3.000 -2.000 9.000 10.00
Mod parameter 3 of component 2 powerlaw norm
1.000 1.0000E-02 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 1.0000E+24 1.0000E+24
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
mo = phabs[1]( powerlaw[2] )
Model Fit Model Component Parameter Unit Value
par par comp
1 1 1 phabs nH 10^22 1.000 +/- 0.0000E+00
2 2 2 powerlaw PhoIndex 1.000 +/- 0.0000E+00
3 3 2 powerlaw norm 1.000 +/- 0.0000E+00
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
3 variable fit parameters
Chi-Squared = 4.7882854E+08 using 125 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 3924824. for 122 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 0.000E+00
Note that we could have chosen all the defaults by entering /* at the first prompt.
The Current statistic is ![]() and is huge for the initial,
default values--mostly because the power law normalization is two
orders of magnitude too large. This is easily fixed using the
renorm command :
and is huge for the initial,
default values--mostly because the power law normalization is two
orders of magnitude too large. This is easily fixed using the
renorm command :
XSPEC> ren Chi-Squared = 873.5161 using 125 PHA bins. Reduced chi-squared = 7.159968 for 122 degrees of freedom Null hypothesis probability = 0.000E+00
We are not quite ready to fit the data (and obtain a better
![]() ), because not all of the 125 PHA
bins should be included in the fitting: some are below the lower
discriminator of the instrument and therefore do not contain valid data;
some have imperfect background
subtraction at the margins of the pass band; and some may not contain
enough counts for
), because not all of the 125 PHA
bins should be included in the fitting: some are below the lower
discriminator of the instrument and therefore do not contain valid data;
some have imperfect background
subtraction at the margins of the pass band; and some may not contain
enough counts for ![]() to be strictly meaningful. To find out
which channels to discard (ignore in XSPEC terminology),
users must consult mission-specific documentation, which will inform them
of discriminator settings, background subtraction problems and other
issues. For the mature missions in the HEASARC archives, this
information already has been encoded in the headers of the spectral
files as a list of ``bad'' channels. Simply issue the command:
to be strictly meaningful. To find out
which channels to discard (ignore in XSPEC terminology),
users must consult mission-specific documentation, which will inform them
of discriminator settings, background subtraction problems and other
issues. For the mature missions in the HEASARC archives, this
information already has been encoded in the headers of the spectral
files as a list of ``bad'' channels. Simply issue the command:
XSPEC> ignore bad Chi-Squared = 821.0203 using 85 PHA bins. Reduced chi-squared = 10.01244 for 82 degrees of freedom Null hypothesis probability = 0.000E+00
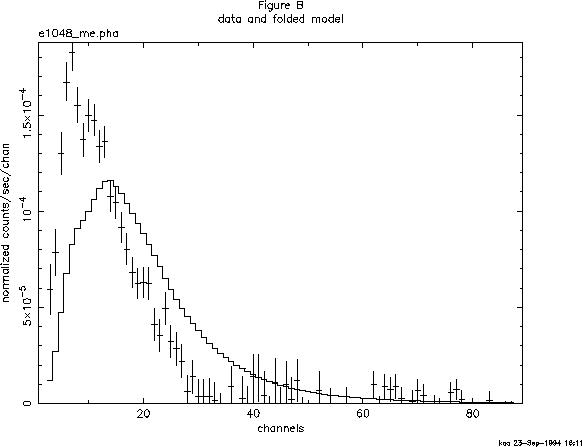
We can see that 40 channels are bad--but do we need to ignore any more? These channels are bad because of certain instrument properties: other channels still may need to be ignored because of the shape and brightness of the spectrum itself. Figure B shows the result of plotting the data in channels (using the commands setplot channel and plot data). We see that above about channel 33 the S/N becomes small. We also see, comparing Figure B with Figure A, which bad channels were ignored. Although visual inspection is not the most rigorous method for deciding which channels to ignore (more on this subject later), it's good enough for now, and will at least prevent us from getting grossly misleading results from the fitting. To ignore channels above 33:
XSPEC> ignore 34-** Chi-Squared = 698.6030 using 31 PHA bins. Reduced chi-squared = 24.95011 for 28 degrees of freedom Null hypothesis probability = 0.000E+00
The same result can be achieved with the command ignore 34-125. The inverse of ignore is notice, which has the same syntax.
We are now ready to fit the data. Fitting is initiated by the command
fit. As the fit proceeds, the screen displays the status of the
fit for each iteration until either the fit converges to the minimum
![]() , or the user is asked whether the fit is to go through
another set of iterations to find the minimum. The default number of
iterations is ten.
, or the user is asked whether the fit is to go through
another set of iterations to find the minimum. The default number of
iterations is ten.
XSPEC> fit
Chi-Squared Lvl Fit param # 1 2 3
42.2976 -4 0.0000E+00 2.097 9.5812E-03
33.3556 -5 0.0000E+00 1.988 8.7573E-03
33.2648 -6 0.0000E+00 1.998 8.8977E-03
33.2620 -7 0.0000E+00 1.997 8.8844E-03
33.2102 -1 0.1054 2.002 9.0267E-03
31.2525 -2 0.1783 2.064 9.9760E-03
30.6874 -3 0.3738 2.170 1.1635E-02
30.1174 -4 0.4242 2.195 1.2241E-02
30.1119 -5 0.4263 2.196 1.2271E-02
Number of trials exceeded - last iteration delta = 5.4607E-03
Continue fitting? (Y)
30.1119 -5 0.4265 2.196 1.2272E-02
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Variances and Principal axes :
1 2 3
4.24E-08 | 0.00 -0.01 1.00
7.54E-02 | -0.90 -0.44 -0.01
2.20E-03 | -0.44 0.90 0.01
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
mo = phabs[1]( powerlaw[2] )
Model Fit Model Component Parameter Unit Value
par par comp
1 1 1 phabs nH 10^22 0.4265 +/- 0.2478
2 2 2 powerlaw PhoIndex 2.196 +/- 0.1271
3 3 2 powerlaw norm 1.2272E-02 +/- 0.2423E-02
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chi-Squared = 30.11190 using 31 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 1.075425 for 28 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 0.358
The fit is good: reduced ![]() is 1.075 for 31 - 3 = 28 degrees of
freedom. The null hypothesis probability is the probability of getting
a value of
is 1.075 for 31 - 3 = 28 degrees of
freedom. The null hypothesis probability is the probability of getting
a value of ![]() as large or larger than observed if the model is
correct. If this probability is small then the model is not a good
fit. The matrix of principal
axes printed out at the end of a fit provides an indication of whether
parameters are correlated (at least local to the best fit). In this
example the powerlaw norm is not correlated with any other parameter
while the column and powerlaw index are slightly correlated.
as large or larger than observed if the model is
correct. If this probability is small then the model is not a good
fit. The matrix of principal
axes printed out at the end of a fit provides an indication of whether
parameters are correlated (at least local to the best fit). In this
example the powerlaw norm is not correlated with any other parameter
while the column and powerlaw index are slightly correlated.
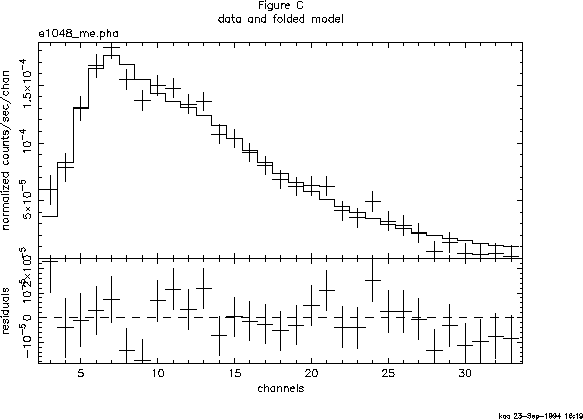
To see the fit and the residuals, we can use the command plot data resid. The result is shown in Figure C.
The screen output shows the best-fitting parameter values, as well as approximations to their errors. These errors should be regarded as indications of the uncertainties in the parameters and should not be quoted in publications. The true errors, i.e. the confidence ranges, are obtained using the error command:
XSPEC> error 1 2 3
Parameter Confidence Range ( 2.706)
1 3.036326E-02 0.858369
2 1.99421 2.41126
*WARNING*:RENORM: No variable model to allow renormalization
*WARNING*:RENORM: No variable model to allow renormalization
*WARNING*:RENORM: No variable model to allow renormalization
*WARNING*:RENORM: No variable model to allow renormalization
*WARNING*:RENORM: No variable model to allow renormalization
*WARNING*:RENORM: No variable model to allow renormalization
*WARNING*:RENORM: No variable model to allow renormalization
*WARNING*:RENORM: No variable model to allow renormalization
*WARNING*:RENORM: No variable model to allow renormalization
3 8.949995E-03 1.716900E-02
Here, the numbers 1, 2, 3 refer to the parameter numbers in the Model
par column of the screen output. For the first parameter, the column of
absorbing hydrogen atoms, the 90%
confidence range is ![]() cm
cm ![]() . This corresponds to an
excursion in
. This corresponds to an
excursion in ![]() of 2.706. The reason these ``better'' errors are
not given automatically as part of the fit output is that they
entail further fitting. When the model is simple, this does not require
much CPU, but for complicated models the extra time can be
considerable. The warning message is generated because there are
no free normalizations in the model while the error is being
calculated on the normalization itself. In this case, the warning may
safely be ignored.
of 2.706. The reason these ``better'' errors are
not given automatically as part of the fit output is that they
entail further fitting. When the model is simple, this does not require
much CPU, but for complicated models the extra time can be
considerable. The warning message is generated because there are
no free normalizations in the model while the error is being
calculated on the normalization itself. In this case, the warning may
safely be ignored.
What else can we do with the fit? One thing is to derive the flux of the model. The data by themselves only give the instrument-dependent count rate. The model, on the other hand, is an estimate of the true spectrum emitted. In XSPEC, the model is defined in physical units independent of the instrument. The command flux integrates the current model over the range specified by the user:
XSPEC> flux 2 10 Model flux 3.5495E-03 photons ( 2.2492E-11 ergs)cm**-2 s**-1 ( 2.000- 10.000)
Here, we have chosen the standard X-ray range of 2-10 keV and find that
the energy flux is ![]() erg cm
erg cm ![]() s
s ![]() . Note
that flux will integrate only within the energy range of the
current response matrix. If the model flux outside this range is
desired--in effect, an extrapolation beyond the data--then the command
dummyrsp should be used. This command sets up a dummy response
that covers the range required. For example, if we want to know the flux
of our model in the ROSAT PSPC band of 0.2-2 keV, we enter:
. Note
that flux will integrate only within the energy range of the
current response matrix. If the model flux outside this range is
desired--in effect, an extrapolation beyond the data--then the command
dummyrsp should be used. This command sets up a dummy response
that covers the range required. For example, if we want to know the flux
of our model in the ROSAT PSPC band of 0.2-2 keV, we enter:
XSPEC> dummyrsp 0.2 2. Chi-Squared = 3583.779 using 31 PHA bins. Reduced chi-squared = 127.9921 for 28 degrees of freedom Null hypothesis probability = 0.000E+00 XSPEC> flux 0.2 2. Model flux 4.5514E-03 photons ( 9.1372E-12 ergs)cm**-2 s**-1 ( 0.200- 2.000)
The energy flux, at ![]() erg cm
erg cm ![]() s
s ![]() , is
lower in this band but the photon flux is higher. To get our original
response matrix back we enter :
, is
lower in this band but the photon flux is higher. To get our original
response matrix back we enter :
XSPEC> response Chi-Squared = 30.11190 using 31 PHA bins. Reduced chi-squared = 1.075425 for 28 degrees of freedom Null hypothesis probability = 0.358
The fit, as we've remarked, is good, and the parameters are constrained. But unless the purpose of our investigation is merely to measure a photon index, it's a good idea to check whether alternative models can fit the data just as well. We also should derive upper limits to components such as iron emission lines and additional continua, which, although not evident in the data nor required for a good fit, are nevertheless important to constrain. First, let's try an absorbed black body:
XSPEC> mo pha(bb)
mo = phabs[1]( bbody[2] )
Input parameter value, delta, min, bot, top, and max values for ...
Mod parameter 1 of component 1 phabs nH 10^22
1.000 1.0000E-03 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 1.0000E+05 1.0000E+06
/*
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
mo = phabs[1]( bbody[2] )
Model Fit Model Component Parameter Unit Value
par par comp
1 1 1 phabs nH 10^22 1.000 +/- 0.0000E+00
2 2 2 bbody kT keV 3.000 +/- 0.0000E+00
3 3 2 bbody norm 1.000 +/- 0.0000E+00
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
3 variable fit parameters
Chi-Squared = 3.2851246E+09 using 31 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 1.1732588E+08 for 28 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 0.000E+00
XSPEC> fit
Chi-Squared Lvl Fit param # 1 2 3
1282.25 0 0.0000E+00 2.716 6.6520E-04
1224.83 0 0.0000E+00 2.581 6.1010E-04
1156.77 0 0.0000E+00 2.436 5.6200E-04
1079.60 0 0.0000E+00 2.287 5.1647E-04
992.095 0 0.0000E+00 2.134 4.7358E-04
892.988 0 0.0000E+00 1.977 4.3356E-04
781.499 0 0.0000E+00 1.818 3.9681E-04
658.184 0 0.0000E+00 1.657 3.6384E-04
526.528 0 0.0000E+00 1.498 3.3542E-04
Number of trials exceeded - last iteration delta = 131.7
Continue fitting? (Y)
395.283 0 0.0000E+00 1.345 3.1255E-04
362.585 -1 0.0000E+00 0.9723 2.0901E-04
...
114.035 -30 0.0000E+00 0.8905 2.7727E-04
113.954 0 0.0000E+00 0.8904 2.7858E-04
113.954 -1 0.0000E+00 0.8904 2.7864E-04
113.954 0 0.0000E+00 0.8905 2.7863E-04
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Variances and Principal axes :
2 3
2.87E-04 | -1.00 0.00
8.47E-11 | 0.00 -1.00
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
mo = phabs[1]( bbody[2] )
Model Fit Model Component Parameter Unit Value
par par comp
1 1 1 phabs nH 10^22 0.0000E+00 +/- -1.000
2 2 2 bbody kT keV 0.8905 +/- 0.1694E-01
3 3 2 bbody norm 2.7863E-04 +/- 0.9266E-05
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chi-Squared = 113.9543 using 31 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 4.069796 for 28 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 2.481E-12
Note that when more than 10 iterations are required for convergence the user is asked whether or not to continue at the end of each set of 10. Saying no at these prompts is a good idea if the fit is not converging quickly. Conversely, to avoid having to keep answering the question, i.e., to increase the number of iterations before the prompting question appears, begin the fit with, say:
XSPEC> fit 100
This command will put the fit through 100 iterations before pausing.
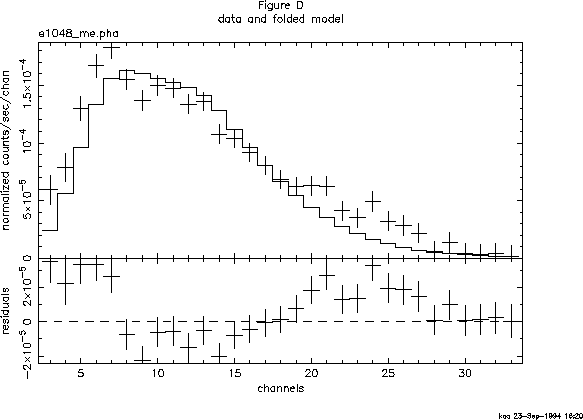
The black body fit is obviously not a good one. Not only is ![]() large, but the best-fitting
large, but the best-fitting ![]() is rather low. Inspection of the
residuals confirms this: the pronounced wave-like shape is indicative of
a bad choice of overall continuum (see Figure D). Let's try thermal
bremsstrahlung next:
is rather low. Inspection of the
residuals confirms this: the pronounced wave-like shape is indicative of
a bad choice of overall continuum (see Figure D). Let's try thermal
bremsstrahlung next:
XSPEC> mo pha(br)
mo = phabs[1]( bremss[2] )
Input parameter value, delta, min, bot, top, and max values for ...
Mod parameter 1 of component 1 phabs nH 10^22
1.000 1.0000E-03 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 1.0000E+05 1.0000E+06
/*
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
mo = phabs[1]( bremss[2] )
Model Fit Model Component Parameter Unit Value
par par comp
1 1 1 phabs nH 10^22 1.000 +/- 0.0000E+00
2 2 2 bremss kT keV 7.000 +/- 0.0000E+00
3 3 2 bremss norm 1.000 +/- 0.0000E+00
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
3 variable fit parameters
Chi-Squared = 4.4153124E+07 using 31 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 1576897. for 28 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 0.000E+00
XSPEC> fit
Chi-Squared Lvl Fit param # 1 2 3
30.4999 -4 0.0000E+00 4.909 8.4675E-03
28.1488 -5 0.0000E+00 5.329 8.2510E-03
28.0226 -6 0.0000E+00 5.360 8.2807E-03
28.0222 -7 0.0000E+00 5.360 8.2778E-03
28.0222 4 0.0000E+00 5.360 8.2778E-03
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Variances and Principal axes :
2 3
1.68E-01 | -1.00 0.00
2.31E-08 | 0.00 -1.00
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
mo = phabs[1]( bremss[2] )
Model Fit Model Component Parameter Unit Value
par par comp
1 1 1 phabs nH 10^22 0.0000E+00 +/- -1.000
2 2 2 bremss kT keV 5.360 +/- 0.4104
3 3 2 bremss norm 8.2778E-03 +/- 0.3402E-03
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chi-Squared = 28.02222 using 31 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 1.000794 for 28 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 0.268
Bremsstrahlung is a better fit than the black body--and is as good as
the power law--although it shares the low ![]() . With two good fits,
the power law and the bremsstrahlung, it's time to scrutinize their
parameters in more detail.
. With two good fits,
the power law and the bremsstrahlung, it's time to scrutinize their
parameters in more detail.
From the EXOSAT database on HEASARC, we know that the target in
question, 1E1048.1-5937, has a Galactic latitude of 24 arcmin, i.e.,
almost on the plane of the Galaxy. In fact, the data base also provides
the value of the Galactic ![]() based on 21-cm radio observations. At
based on 21-cm radio observations. At
![]() cm
cm ![]() , it is higher than the 90 percent-confidence upper
limit from the power-law fit. Perhaps, then, the power-law fit is not so
good after all. What we can do is fix (freeze in XSPEC
terminology) the value of
, it is higher than the 90 percent-confidence upper
limit from the power-law fit. Perhaps, then, the power-law fit is not so
good after all. What we can do is fix (freeze in XSPEC
terminology) the value of ![]() at the Galactic value and refit the
power law. Although we won't get a good fit, the shape of the residuals
might give us a clue to what is missing. To freeze a parameter in
XSPEC, use the command freeze followed by the parameter number,
like this:
at the Galactic value and refit the
power law. Although we won't get a good fit, the shape of the residuals
might give us a clue to what is missing. To freeze a parameter in
XSPEC, use the command freeze followed by the parameter number,
like this:
XSPEC> freeze 1 Number of variable fit parameters = 2
The inverse of freeze is thaw:
XSPEC> thaw 1 Number of variable fit parameters = 3
Alternatively, parameters can be frozen using the newpar command,
which allows all the quantities associated with a parameter to be
changed. The second quantity, delta, is the step size used to
calculate the derivative in the fitting, and, if set to a negative
number, will cause the parameter to
be frozen. In our case, we want ![]() frozen at
frozen at
![]() cm
cm ![]() , so we go back to the power law best fit
and do the following :
, so we go back to the power law best fit
and do the following :
XSPEC> newpar 1
Input parameter value, delta, min, bot, top, and max values for ...
Mod parameter 1 of component 1 phabs nH 10^22
0.4265 1.0000E-03 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 1.0000E+05 1.0000E+06
4,0
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
mo = phabs[1]( powerlaw[2] )
Model Fit Model Component Parameter Unit Value
par par comp
1 1 1 phabs nH 10^22 4.000 frozen
2 2 2 powerlaw PhoIndex 2.196 +/- 0.1271
3 3 2 powerlaw norm 1.2272E-02 +/- 0.2423E-02
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
2 variable fit parameters
Chi-Squared = 918.0695 using 31 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 31.65757 for 29 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 0.000E+00
Note the useful trick of giving a value of zero for delta in the newpar command. This has the effect of changing delta to the negative of its current value. If the parameter is free, it will be frozen, and if frozen, thawed. The same result can be obtained by putting everything onto the command line, i.e., newpar 1 4, 0, or by issuing the two commands, newpar 1 4 followed by freeze 1. Now, if we fit again, we get the following set of parameters:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
mo = phabs[1]( powerlaw[2] )
Model Fit Model Component Parameter Unit Value
par par comp
1 1 1 phabs nH 10^22 4.000 frozen
2 2 2 powerlaw PhoIndex 3.734 +/- 0.6937E-01
3 3 2 powerlaw norm 0.1451 +/- 0.1202E-01
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chi-Squared = 140.3156 using 31 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 4.838470 for 29 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 1.515E-16
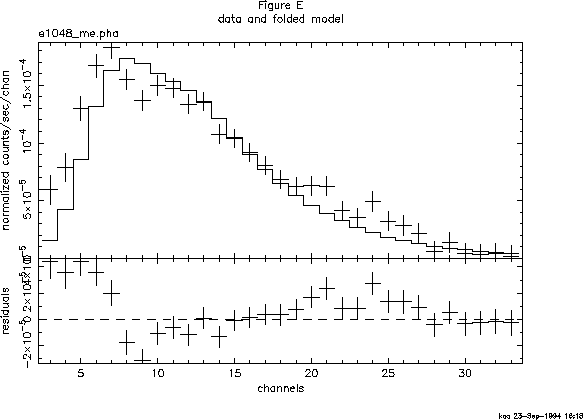
The fit is not good. In Figure E we can see why: there appears to be a surplus of softer photons, perhaps indicating a second continuum component. To investigate this possibility we can add a component to our model. The editmod command lets us do this without having to respecify the model from scratch. Here, we'll add a black body component.
XSPEC> editmod pha(po+bb)
mo = phabs[1]( powerlaw[2] + bbody[3] )
Input parameter value, delta, min, bot, top, and max values for ...
Mod parameter 4 of component 3 bbody kT keV
3.000 1.0000E-02 1.0000E-04 1.0000E-02 100.0 200.0
2,0
Mod parameter 5 of component 3 bbody norm
1.000 1.0000E-02 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 1.0000E+24 1.0000E+24
1.e-5
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
mo = phabs[1]( powerlaw[2] + bbody[3] )
Model Fit Model Component Parameter Unit Value
par par comp
1 1 1 phabs nH 10^22 4.000 frozen
2 2 2 powerlaw PhoIndex 3.734 +/- 0.6937E-01
3 3 2 powerlaw norm 0.1451 +/- 0.1202E-01
4 4 3 bbody kT keV 2.000 frozen
5 5 3 bbody norm 1.0000E-05 +/- 0.0000E+00
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
3 variable fit parameters
Chi-Squared = 136.4535 using 31 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 4.873339 for 28 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 3.211E-16
Notice that in specifying the initial values of the black body, we have frozen kT at 2 keV (the canonical temperature for nuclear burning on the surface of a neutron star in a low-mass X-ray binary) and started the normalization at zero. Without these measures, the fit might ``lose its way''. Now, if we fit, we get (not showing all the iterations this time):
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
mo = phabs[1]( powerlaw[2] + bbody[3] )
Model Fit Model Component Parameter Unit Value
par par comp
1 1 1 phabs nH 10^22 4.000 frozen
2 2 2 powerlaw PhoIndex 5.149 +/- 0.1593
3 3 2 powerlaw norm 0.5117 +/- 0.7427E-01
4 4 3 bbody kT keV 2.000 frozen
5 5 3 bbody norm 2.4748E-04 +/- 0.3857E-04
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chi-Squared = 60.03419 using 31 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 2.144078 for 28 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 4.032E-04
The fit is better than the one with just a power law and the fixed Galactic column, but it is still not good. Thawing the black body temperature and fitting gives us:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
mo = phabs[1]( powerlaw[2] + bbody[3] )
Model Fit Model Component Parameter Unit Value
par par comp
1 1 1 phabs nH 10^22 4.000 frozen
2 2 2 powerlaw PhoIndex 6.718 +/- 0.3798
3 3 2 powerlaw norm 1.613 +/- 0.4485
4 4 3 bbody kT keV 1.175 +/- 0.7791E-01
5 5 3 bbody norm 2.8019E-04 +/- 0.3361E-04
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chi-Squared = 38.83833 using 31 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 1.438457 for 27 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 6.554E-02
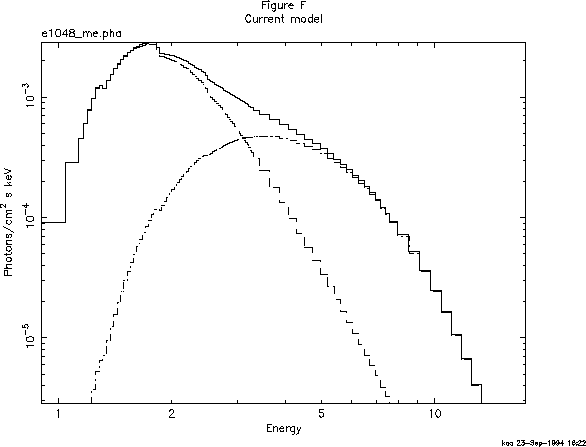
This, of course, is a better fit, but the photon index of the power law has ended up extremely and implausibly steep. Looking at this odd model (with the command plot model), we see, in Figure F, that the black body and the power law have changed places, in that the power law provides the soft photons required by the high absorption, while the black body provides the harder photons.
We could continue to search for a plausible, well-fitting model, but the data, with their limited signal-to-noise and energy resolution, probably don't warrant it (the original investigators published only the power law fit). There is, however, one final, useful thing to do with the data: derive an upper limit to the presence of a fluorescent iron emission line. First we delete the black body component using delcomp:
XSPEC> delcomp 3 mo = phabs[1]( powerlaw[2] ) Chi-Squared = 1314.765 using 31 PHA bins. Reduced chi-squared = 45.33672 for 29 degrees of freedom Null hypothesis probability = 0.000E+00
Then we thaw ![]() and refit to recover our original, best fit (output
not shown). Then, we add a gaussian emission line of fixed energy and
width:
and refit to recover our original, best fit (output
not shown). Then, we add a gaussian emission line of fixed energy and
width:
XSPEC> editmod pha(po+ga)
mo = phabs[1]( powerlaw[2] + gaussian[3] )
Input parameter value, delta, min, bot, top, and max values for ...
Mod parameter 4 of component 3 gaussian LineE keV
6.500 5.0000E-02 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 1.0000E+06 1.0000E+06
6.4 0
Mod parameter 5 of component 3 gaussian Sigma keV
0.1000 5.0000E-02 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 10.00 20.00
0.1 0
Mod parameter 6 of component 3 gaussian norm
1.000 1.0000E-02 0.0000E+00 0.0000E+00 1.0000E+24 1.0000E+24
1.e-4
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
mo = phabs[1]( powerlaw[2] + gaussian[3] )
Model Fit Model Component Parameter Unit Value
par par comp
1 1 1 phabs nH 10^22 0.4266 +/- 0.2479
2 2 2 powerlaw PhoIndex 2.196 +/- 0.1271
3 3 2 powerlaw norm 1.2273E-02 +/- 0.2425E-02
4 4 3 gaussian LineE keV 6.400 frozen
5 5 3 gaussian Sigma keV 0.1000 frozen
6 6 3 gaussian norm 1.0000E-04 +/- 0.0000E+00
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
4 variable fit parameters
Chi-Squared = 32.73828 using 31 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 1.212569 for 27 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 0.206
The energy and width have to be frozen because,in the absence of an obvious line in the data, the fit would be completely unable to converge on meaningful values. Besides, our aim is to see how bright a line at 6.4 keV can be and still not ruin the fit. To do this, we fit first and then use the error command to derive the maximum allowable iron line normalization. We then set the normalization at this maximum value with newpar and, finally, derive the equivalent width using the eqwidth command. That is:
XSPEC> err 6
Parameter Confidence Range ( 2.706)
Parameter pegged at hard limit 0.0000E+00
with delta ftstat= 0.4853
6 0.000000E+00 1.587037E-04
XSPEC> new 6 1.587037E-04
4 variable fit parameters
Chi-Squared = 35.75737 using 31 PHA bins.
Reduced chi-squared = 1.324332 for 27 degrees of freedom
Null hypothesis probability = 0.121
XSPEC> eqwidth 3
Additive group equiv width for model 3 (gaussian): 870. eV
Things to note: