


Next: How to contact us
Up: Introduction
Previous: XSPEC
The following list summarizes the major changes to XSPEC since the
previous edition of the user's manual.
- Tcl now provides the user interface. This should be mostly
transparent to the user except that more options are available
(see appendix D for details). There are a few changes that
are required
- exec command or command should be used
instead of $ command.
- xhistory should be used rather than history.
- recall and reexecute have been replaced by
history and !n (to reexecute command n).
- The XCOMS environment variable no longer works as a
list of directories in which to search for script files.
- The XSPEC initialization script is called .xspecrc and
must reside in the user's home directory.
- Since the PLT commands are not yet integrated into the
Tcl environment it is not possible to write a script
containing iplot and then some PLT commands. Instead,
use setplot com and plot.
- The setplot command cannot be abbreviated to set
but must be at least setp.
- Dynamic memory is now used. This means that
- XSPEC now requires much less memory on start-up and the
amount of memory used will depend on the sizes of the
datasets and response matrices read in.
- Most of the arbitrary limits on the sizes of files have
been removed.
- Some sections of XSPEC have been sped-up.
- There is a new, improved makefile which does incremental builds
correctly. To force a complete new build use xmake full.
- The response matrix reading has been updated to use the TLMIN4
keyword in the RESPONSE extension (mainly for use with XTE
HEXTE files).
- If setplot wave has been specified and an ignore or
notice command is given with real numbers then these specify
wavelengths in Angstrom. For setplot chan and setplot energy
the real numbers represent energies in keV.
- The algorithm for the error or uncertainty command has
been improved and should be faster and more reliable.
- A bug that caused incorrect estimated parameter uncertainties
for the C-stat has been fixed.
- At the end of a fit run XSPEC now writes out the principal
axes of the error ellipsoid. This can give some clues about
which parameters are correlated.
- All parameters have units specified.
- XSPEC now automatically writes out its current state to
the file xautosav.xcm. The default is to write out the
state after every command. The autosave command can change
the frequency of updating of xautosav.xcm or turn it off
completely.
- The editmod command enables the user to add, delete, or
replacement any one component in the model.
- The dummyrsp command has additional arguments which
allow the creation of a virtual response matrix with perfect
resolution and efficiency.
- The abund command has two new options. abund aneb
uses the Anders & Ebihara (1982) relative abundances and
abund file filename reads a set of relative abundances
from filename.
- The extra page is no longer produced when specifying PostScript
devices using the XSPEC cpd command.
- Three new plot options are available :
- eemodel plots the model in
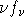 space.
space. - eeufspec plots the unfolded spectrum in
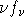 space.
space. - dem plots the differential emission measure
distribution for the last multiple temperature model
calculated.
- The slow plotting of spectra with many channels has been fixed.
- plot summary now works correctly and plot eff has
wavelength as the x-axis if setplot wave is used.
- The algebraic format for specifying models is the default. It
is now possible to specify additive components outside the
overall multiplicative group. The algebraic format is used
internally by XSPEC so in some cases the actual order of
components and hence parameters will be different. A tool is
available to convert v9 scripts into v10 scripts.
- The addcomp command has been modified to reflect the change
in the model format.
- Table models must now be specified as e.g.
atable{filename} instead of
atable filename. - A new type of model is available. Convolution models are
generalizations of multiplicative models and allow more
complicated operations than simple multiplications. A gaussian
smoothing model (gsmooth) is included as an example.
- The following new models have been added and old ones improved:
- grbm is a gamma-ray burst spectrum (after Band).
- c6mekl, c6pmekl, c6vmekl,
and c6pvmkl supersede cp6mkl and cp6vmkl.
- laor is an emission line from a disk around a black
hole.
- plcabs is an approximation for transmission through
Compton-thick matter.
- gsmooth is a convolution model to modify the
current model by a Gaussian smoothing.
- vphabs is a photoelectric absorption with variable
abundances.
- zvphabs is a redshifted photoelectric absorption
with variable abundances.
- All mekal based models have a new parameter called
switch which sets whether the model spectrum is
interpolated from a table or calculated (former is
faster, latter is more accurate). The interpolation
option can make up to a factor of 100 difference in speed.
- nteea, pexrav, pexriv, and tita_a
have all been improved.
- pliref, plrefl, and zplrefl have been
removed since they were inaccurate. pexrav and
pexriv should be used in their place.
- mkcflow and vmcflow use the mekal rather
than meka model.
- posm is a model for positronium continuum.
- The model.dat and lmodel.dat files have been
simplified and msetup made more robust. For the
change to lmodel.dat see the example file in the
release. lmodel.dat and the local model source files
can be placed in any directory. The XSPEC make procedure
uses the environment variable LMODDIR to find the directory
containing local models.



Next: How to contact us
Up: Introduction
Previous: XSPEC
Keith Arnaud (kaa@genji.gsfc.nasa.gov)
Wed May 28 10:59:33 EDT 1997
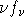 space.
space.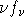 space.
space.