Exponentially cut off power law spectrum reflected from ionized material
(Magdziarz & Zdziarski MNRAS, 273, 837; 1995). Ionization and
opacities of the reflecting medium is computed as in the procedure absori.
The output spectrum is the sum of the cutoff power law and the reflection
component. The reflection component alone can be obtained for rel_refl < 0.
Then the actual reflection normalization is |rel_refl|. Note that you need
to change then the limits of rel_refl excluding zero (as then the direct
component appears). If ![]() , there is no cutoff in the power law. The
metal and iron abundances are variable. Send questions or comments to
aaz@camk.edu.pl.
, there is no cutoff in the power law. The
metal and iron abundances are variable. Send questions or comments to
aaz@camk.edu.pl.
par1 =, power law photon index,
prop. to
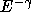
par2 =
, the cutoff energy in keV (if
there is no cutoff;
one needs to change the lower limit for that)
par3 = rel_refl, scaling factor for reflection; if <0, no direct component
(rel_refl=1 for isotropic source above disk)
par4 = redshift, z
par5 = abundance of elements heavier than He relative to the Solar
abundances
par6 = iron abundance relative to the solar iron abundance (7.52)
par7 = cosine of inclination angle
par8 = disk temperature in K
par9 = disk ionization parameter (
)
K = photon flux at 1 keV of the power-law only in the observed frame.